How Do You Know Which Christmas Light Is Out

For beach-goers, experts e'er recommend a good for you blanket of sunscreen to protect the skin from those pesky ultraviolet (UV) rays. But sunlight contains more than just UV light. In fact, it's made upward of ruby, green, yellow, blue and orange light rays, which combine to create "white light" (a.thou.a. sunlight). If you haven't sat through a high school chemistry form in a while, no worries. We'll break down the important stuff — without getting as well scientific.
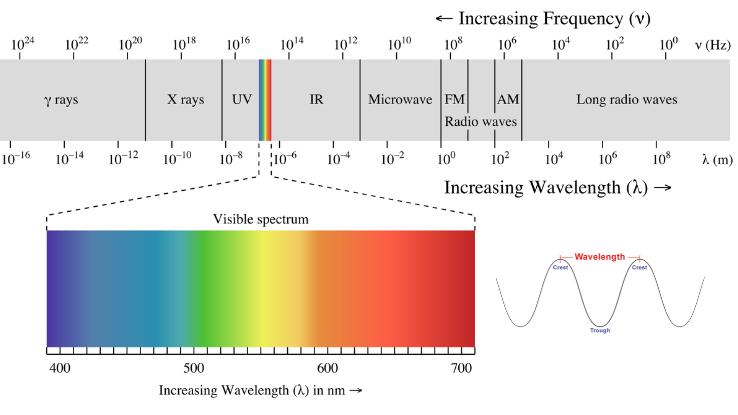
As the name suggests, visible light can be seen by the human eye, and each ray reflects a particular colour. The color of a given ray depends on said ray's wavelength (see the graphic below) — or the distance between successive crests of a wave. (Side note: This means that objects get their colors through the wavelength of the low-cal that is reflected from them. Trust us — don't recollect too difficult most it. Things become trippy.)
Some other important human relationship to annotation is that of wavelengths and energy: The longer the distance between waves, the less free energy a ray has to offer. Think of it this manner — if the wave crests are farther apart, they're a fleck lackadaisical, but if the crests come in rapid succession, there'due south a frenzy of energy there. All of this means rays on the blood-red end of the visible lite spectrum have longer wavelengths and less energy, whereas rays on the blueish cease have shorter wavelengths and more energy.
UV rays, which aren't on the visible light spectrum, surpass bluish light in terms of how much free energy they contain. That incredible corporeality of energy is how those rays are able to create a physical change, like tanning (or called-for) one's skin. In moderation ultraviolet radiation tin be good for us (think vitamin D!), but, on the other hand, information technology can also produce some devastating effects (think sunburn and snow blindness!).
How Does Blue Light Bear on 1's Health?
But what about bluish light — these visible rays that are a few notches below harmful UV rays? Well, approximately one-third of all visible light is considered high-energy visible (HEV) blue light. Blue lite is literally why the sky appears blue: These rays scatter more hands than other visible rays of light when they strike the temper'south air and water molecules — and all that handful makes the sky that vibrant blue.
There's no escaping it, peculiarly considering daylight is our main source of blue light. Only information technology'southward not all bad: Experiencing blue light during the daytime helps regulate one's circadian rhythms, makes one more alert, elevates cognitive function, promotes good think and is even used in light therapy to treat seasonal melancholia disorder (Sad). Notwithstanding, human being-made objects — including LED lights and brandish screens on flat-screen TVs, computers and smartphones — emit blue light too. Although these devices only emit a fraction of the blue light the sun emits, researchers and doctors have still voiced concerns about patients' excessive screen fourth dimension in recent years.
Perhaps surprisingly, the human eye is pretty great at protecting the retina from UV rays, but blue light is a dissimilar story. Virtually all of it penetrates the light-sensitive retina, causing impairment that approximates macular degeneration — a status that can lead to vision loss.
In add-on to potentially harming your eyes over time, bluish low-cal can also lead to eye strain. If yous've ever concluded upwards with a wicked headache afterward staring intensely at an Excel spreadsheet for hours, you're probably familiar with that particular discomfort. When we noted how blue light contributes to the sky looking blue, we mentioned that this is and so because of how blue lite scatters. Well, according to All About Vision, this same scattering of the blue calorie-free that emanates from screens makes for "unfocused visual 'noise' [that] reduces contrast and can contribute to digital eye strain."
If you lot don't suffer from middle strain due to increased exposure to blue lite, these inescapable rays may withal take adverse effects on your wellness. Any sort of light — regardless of where information technology falls on the spectrum — can suppress the human body's ability to release melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep cycles. Nonetheless, information technology's idea that blue lite quashes melatonin secretion even more than than other hues exercise. Researchers at Harvard University compared the effects of bluish and green low-cal exposure and found that "blueish low-cal suppresses melatonin [secretion] for nigh twice as long as the green calorie-free and shifted circadian rhythms by twice as much."
BluTech, a company that manufactures special blue low-cal-filtering lenses, reports that "43% of adults have a job that requires prolonged apply of a tablet or figurer" — and that's just while said adults are on the clock. Factor in all that time nosotros spend online, texting and marathoning Netflix, and adults spend roughly 12 hours a day looking at screens and taking in blue lite. And so, how tin can you mitigate the harmful effects of prolonged exposure to blue low-cal?

Well, these blue light-filtering lenses are becoming all the rage. Although not equally ubiquitous every bit Away suitcases or Blue Frock commercials, you've probably heard commercials for blue light-filtering specs from Felix Gray or Warby Parker on your favorite podcast or radio talk show. Felix Grayness glasses, for instance, pride themselves on having a bluish light-filtering fabric embedded inside, which the visitor says will curb eye strain, headaches and slumber disruption.
If you're not into the spectacles route, experts recommend taking screen breaks, both at work and at home; keeping screens clean to reduce glare and further eye strain; irresolute your annoying white display groundwork to something less bright; blinking more often; and fugitive screens for at to the lowest degree 30 minutes to an hour before bed because screens stimulate your brain. Maybe it's time to trade that fancy bluish low-cal-emitting tablet for a Kindle Paperwhite, or, you know, a skilful sometime-fashioned book.
Source: https://www.faqtoids.com/health/blue-light-facts?utm_content=params%3Ao%3D740006%26ad%3DdirN%26qo%3DserpIndex
0 Response to "How Do You Know Which Christmas Light Is Out"
Post a Comment